Osteoarthritis(osteoarthritis) is a dystrophic joint disease associated with slow degeneration and destruction of intra-articular cartilage. Over time, there is a restructuring of the articular ends of the bones, inflammation and degeneration of the periarticular tissues. The concept of "arthrosis" (deforming osteoarthritis) includes a group of joint diseases of degenerative-inflammatory nature, which have different origins and similar mechanisms.
Causes
Primary arthrosis on the background of age and / or biomechanical changes. Secondarily, it occurs after an injury, on the background of diabetes mellitus or thyroid disease, due to vascular disorders, etc. It contributes to the damage of the ankles and the development of arthrosis of the flat feet, which violates the functions of absorbing the impact of the foot. Timely application of specially selected orthopedic insoles enables correction of foot deformities and reduction of joint load.
Osteoarthritis is the most common joint disease, and the incidence increases with age. But this disease does not occur only in the elderly, which determines its social significance.
Symptoms:
- pain during exertion, disappears at rest;
- restriction of mobility and creaking in the joint;
- muscle tension in the joint area;
- possible periodic swelling, gradual deformation of the joint.
Primary arthrosis - 40-50% of cases of arthrosis. The disease develops on a previously healthy joint, and its cause is not joint damage, but, for example, hard physical work.
Secondary arthrosis - 50-60% of cases. The joint, prone to osteoarthritis, is deformed even before the disease - for example, as a result of trauma.
Which joints are affected by osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis most often develops in the joints of the lower half of the body (hip, knee, first metatarsophalangeal). On the hands, the joints of the phalanges of the fingers are most often exposed to arthrosis. Osteoarthritis usually occurs first on one joint and then on the other - symmetrically to the first.
Coxarthrosis
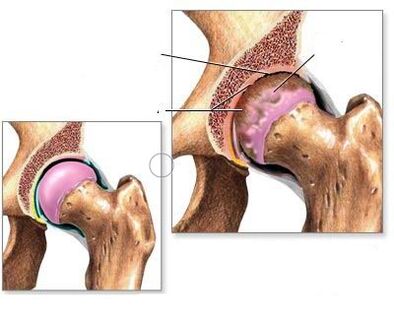
Coxarthrosis(osteoarthritis of the hip joint) is characterized by a progressive course and impaired statodynamic function of the musculoskeletal system. It occupies one of the first places among degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the musculoskeletal system. The dystrophic process begins with articular cartilage - its thinning, dissociation, fragmentation occur and its cushioning properties are lost. As a compensatory reaction of the articular surfaces of the hip joint, marginal bone growths are formed. In the future, sclerosis develops and cysts form in the articular parts of the head of the femur and acetabulum.
Gonarthrosis
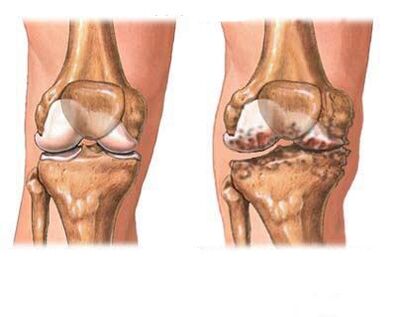
Gonarthrosisosteoarthritis of the knee joint) occupies a leading position in the group of arthritic lesions of the joints of the extremities. Patients with gonarthrosis are constantly prevalent among patients attending polyclinics, but, unfortunately, they are rare among those treated in our hospitals. Inpatient treatment could have a much greater effect than outpatient therapy in the workplace. Known to doctors for more than 100 years, this disease is called "salt deposition" in everyday life.

















































